Venezuela’s stock market crash of 2023 sent shockwaves through global commodity markets, creating unprecedented challenges for international stone suppliers and construction firms. As the country’s economic crisis deepened, the impact on natural stone market volatility became increasingly evident, with prices fluctuating by up to 40% in key export regions.
The collapse affects not only Venezuela’s substantial marble and granite reserves but also disrupts established supply chains across South America. For industry professionals and investors, this market upheaval represents both significant challenges and strategic opportunities. With Venezuela historically being the world’s fifth-largest exporter of ornamental stone, the crash has forced global buyers to rapidly diversify their sourcing strategies and reevaluate pricing models.
Understanding these market dynamics is crucial for construction firms, architects, and stone industry stakeholders as they navigate the ongoing ripple effects of Venezuela’s economic turbulence.
Venezuela’s Role in the Global Stone Market
Key Venezuelan Stone Resources
Venezuela’s natural stone industry has historically been a significant contributor to the global market, with vast deposits of high-quality marble and granite throughout the country. The Táchira region is particularly notable for its premium white and gray marble varieties, while the Bolivar state produces some of South America’s most sought-after granite deposits.
The country’s marble reserves are characterized by their distinctive veining patterns and durability, making them popular choices for both residential and commercial applications. Venezuelan Blue Pearl granite, extracted from quarries in the southeastern region, has earned international recognition for its unique azure undertones and consistent patterning.
Other significant stone resources include Negro Venezuela granite, known for its deep black coloration with subtle speckling, and Caracas White marble, prized for its crystalline structure and exceptional workability. These premium materials have traditionally commanded strong positions in international markets, particularly in North America and Europe.
Before the economic crisis, Venezuela’s stone industry maintained modern extraction facilities and processing centers, capable of producing high-quality slabs and finished products for both domestic use and export markets.
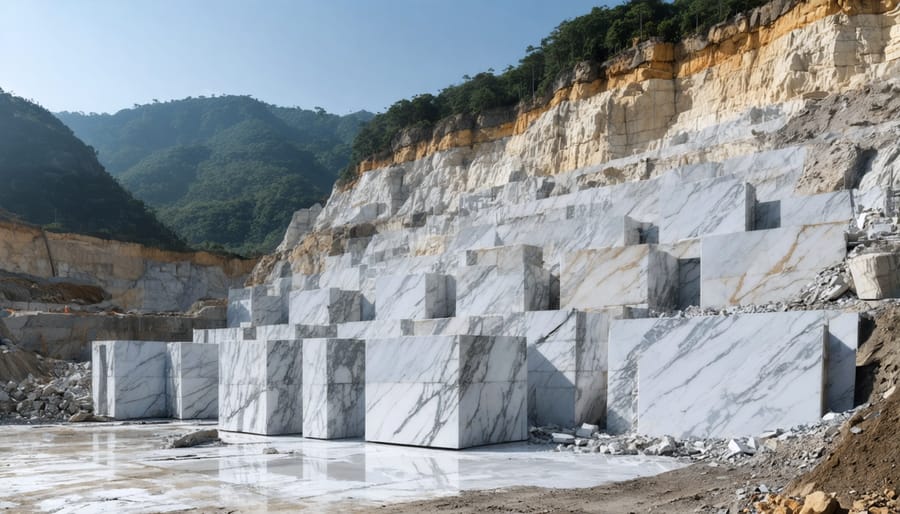

Pre-Crisis Export Statistics
Prior to the economic crisis, Venezuela maintained a robust position in the global stone export market, particularly in marble and granite. During the 2012-2014 period, the country exported approximately 45,000 metric tons of natural stone annually, with primary markets in the United States, Europe, and neighboring Latin American countries. The nation’s stone industry contributed roughly 3% to its non-oil exports, generating an estimated $180 million in annual revenue. Blue Venezuelan granite and cream-colored marble varieties were especially sought after, commanding premium prices in international markets. The country’s strategic location and well-established shipping infrastructure facilitated efficient distribution to major markets, while stable production costs kept Venezuelan stone competitive globally.
The Market Crash’s Direct Impact
Supply Chain Disruptions
The Venezuela stock market crash severely disrupted global stone supply chains, particularly affecting the extraction and distribution of the country’s prestigious marble and granite reserves. Quarry operations faced immediate challenges as investment capital dried up, forcing many smaller operations to suspend activities. Transportation networks, already strained by infrastructure challenges, experienced further setbacks as fuel shortages and currency devaluation made logistics increasingly difficult.
Major stone processing facilities reported operating at just 30-40% capacity during the height of the crisis, leading to significant delays in order fulfillment and increased costs for international buyers. The disruption rippled through the supply chain, affecting construction projects worldwide that relied on Venezuelan stone varieties. Particularly impacted were the popular Blue Macauba granite and Venezuelan Gold marble exports, which saw delivery times extend from typical 6-8 weeks to several months.
These supply chain complications prompted many buyers to seek alternative sources, resulting in a lasting reorganization of traditional stone procurement patterns in the Americas.
Price Fluctuations
The Venezuela stock market crash triggered significant market price fluctuations across various stone categories. Granite prices experienced the most dramatic shifts, with premium varieties seeing up to 30% increases due to supply chain disruptions and heightened demand from alternative markets. Marble, particularly Carrara and Calacatta varieties, showed more stability but still recorded 15-20% price increases as importers sought new supply routes.
Travertine and limestone, traditionally more affordable options, saw moderate price escalations of 10-15%, primarily due to increased shipping costs and supply chain adjustments. Quartzite, which had been gaining popularity before the crisis, maintained relatively stable pricing with only 5-8% increases, thanks to diverse sourcing options outside Venezuela.
Local Venezuelan stone varieties, including Blue Lightning Granite and Platinum White Quartzite, experienced the most severe price volatility, with some materials becoming temporarily unavailable in international markets. This situation prompted many buyers to seek alternative stone options from Brazil, India, and Italy, leading to a redistribution of market demand and subsequent price adjustments across these regions.
Global Market Responses
Alternative Supply Sources
As Venezuela’s stone industry faced disruption, global markets quickly adapted by diversifying their supply sources. Brazil emerged as a leading alternative, leveraging its vast quarries of granite and marble to fill the supply gap. Colombia and Peru also stepped up production, particularly in travertine and limestone varieties, offering competitive pricing and reliable shipping routes.
Stone processors in North America and Europe began developing relationships with emerging suppliers from India and Turkey, known for their extensive marble deposits and modernized extraction techniques. These new partnerships helped stabilize prices and ensure consistent material availability for ongoing projects.
The market adjustment also sparked innovation in material substitution, with some manufacturers introducing engineered stone products and composite materials as alternatives to traditional Venezuelan stone. This diversification not only helped mitigate supply chain risks but also introduced new design possibilities for architects and builders.
Price Stabilization Efforts
In response to the market volatility, Venezuelan authorities implemented several stabilization measures, including temporary trading suspensions and price controls on essential commodities. The central bank introduced currency controls to prevent capital flight, while simultaneously working with major market players to establish trading bands that would limit extreme price fluctuations. These efforts, however, achieved limited success due to the underlying economic challenges and hyperinflation.
Local industry groups formed crisis committees to coordinate responses and maintain some degree of market functionality. Despite these initiatives, trading volumes remained significantly depressed, with many investors seeking alternative markets or moving assets offshore. The government’s attempts to artificially support stock values through state-sponsored buying programs proved unsustainable, ultimately leading to further market distortions and reduced investor confidence in the long-term stability of Venezuelan exchanges.
International financial institutions offered technical assistance for market reforms, though implementation faced significant political and practical hurdles.
Implications for Construction Industry
The Venezuelan stock market crash has significantly impacted the construction industry, particularly affecting project timelines and material selection strategies. Construction companies and developers have been forced to reassess their approaches to material sourcing and project planning due to increased volatility in material costs and supply chain disruptions.
Local construction projects have experienced severe delays as companies struggle with reduced access to financing and increased material costs. The crash has led to a 60% decrease in new construction starts compared to pre-crisis levels, with many existing projects being put on hold or abandoned entirely.
Material selection has become increasingly critical, with contractors focusing on more cost-effective alternatives and locally sourced materials. Natural stone, traditionally imported from Venezuela’s quarries, has seen significant price fluctuations, leading to a shift toward alternative materials or stone sourced from other regions.
The crisis has also influenced construction methodologies, with many firms adopting modular construction techniques and prefabricated components to reduce costs and minimize project risks. This adaptation has helped some companies maintain operations despite challenging market conditions.
International construction companies operating in Venezuela have implemented risk mitigation strategies, including:
– Diversifying material suppliers across multiple countries
– Maintaining larger material inventories
– Incorporating flexible pricing mechanisms in contracts
– Establishing partnerships with local suppliers
These changes have reshaped the construction landscape, forcing industry professionals to become more adaptable and innovative in their approach to project management and material selection. While challenging, these adaptations have led to improved efficiency and more resilient business models within the sector.
The Venezuela stock market crash has significantly reshaped the natural stone industry landscape, creating both challenges and opportunities in the global market. The crisis led to disruptions in supply chains and pricing volatility, particularly affecting Venezuela’s prominent quarries and stone processing facilities. However, the industry has demonstrated remarkable resilience through diversification of sourcing channels and adoption of innovative business strategies.
Looking ahead, market analysts project a gradual stabilization of natural stone prices as alternative suppliers emerge and logistics networks adapt. Industry stakeholders are increasingly focusing on sustainable practices and local sourcing options to mitigate future market disruptions. The development of new extraction technologies and processing methods suggests potential for increased efficiency and cost-effectiveness in the coming years.
For professionals and consumers in the natural stone sector, maintaining flexible procurement strategies and building strong relationships with multiple suppliers will be crucial. While challenges persist, the market’s fundamental strength and growing demand for natural stone products indicate positive long-term prospects, despite the immediate impact of Venezuela’s economic turbulence. Continuous monitoring of market conditions and adaptable business approaches will be key to navigating future uncertainties successfully.










